-
Causes and risk factors of trigger points
In most cases an acute muscle injury or continual muscle stress may lead to the development of trigger points. Trigger points are discrete, focal, hyperirritable spots located in a taut band of skeletal muscle. They produce pain locally and in a referred pattern and often accompany chronic musculoskeletal disorders.
Most points occur because of muscle overuse, muscle trauma (injury), or psychological stress. Trigger points often arise from sustained repetitive activities, like lifting heavy objects at work or working on a computer all day. No single factor is responsible for the development of myofascial trigger points.
For example, a spot within or near a strained muscle may become a trigger point and repetitive motions and poor posture also may increase your risk.
However no single factor is responsible for the development of myofascial trigger points. A combination of contributing factors may include:
- • poor posture
- • sitting for a long time in awkward positions
- • nutritional deficiencies
- • serious lack of exercise or movement
- • any injury to the musculoskeletal system or intervertebral disks
- • generalized fatigue
- • lack of sleep
- • hormonal changes (menopause)
- • intense cooling of muscles (such as when sleeping in front of an air conditioner)
- • emotional problems (depression or anxiety)
- • other pain or inflammation conditions
- • obesity
- • Smoking
Mar 1, 2021 -
Healing osteoarthritis with the use of osteopathy techniques
In Canada Arthritis is the most common chronic health condition, and more than six million Canadians experience the daily impact of arthritis.
Manual therapies such as osteopathy techniques however, can relieve pain, decrease inflammation, increase flexibility and improve quality of life for people with osteoarthritis.
osteopathic treatment can do a great deal to reduce_pain, ease swelling and improve mobility and range of joint movement. We focus on eliminating symptoms through early diagnosis and improving your lifestyle to prevent further degeneration.
Early diagnosis and management are key to preventing further joint damage and improving your quality of life. Diet, maintaining a healthy weight, exercise, stretching techniques and relieving_stress are all lifestyle changes that you can make in order to manage your arthritis symptoms and prevent more joint damage.
Feb 17, 2021 -
Treatments options in 4 stages of osteoarthritis :
- • Stage 0 – There is no treatment required for stage 0 OA except preventive measures and regular sporting activities.
- • Stage 1 – supplements such as glucosamine and chondroition may be recommended. Lifestyle considerations like regular exercise may also prove to be helpful.
- • Stage 2 – There are different nonpharmacologic therapies to help relieve the pain and discomfort caused in this mild stage. These include osteopathic treatment, and also different kinds of physical therapies and life modifications and acupuncture.
- • Stage 3 – Over the counter NSAIDs or pain-relief therapies may be prescribed. If these methods are not effective, the orthopaedic doctor may prescribe stronger pain medicine, such as codeine and oxycodone. Different osteopathic techniques, physical treatments & acupuncture would be very effective too.
- • Stage 4 – In cases of severe OA of th knee, an option is performing osteotomy or bone realignment surgery, or total knee replacement, or arthroplasty. If you are suffering from knee pain, contact your family physician for a proper diagnosis and treatment pain.
Jan 29, 2021 -
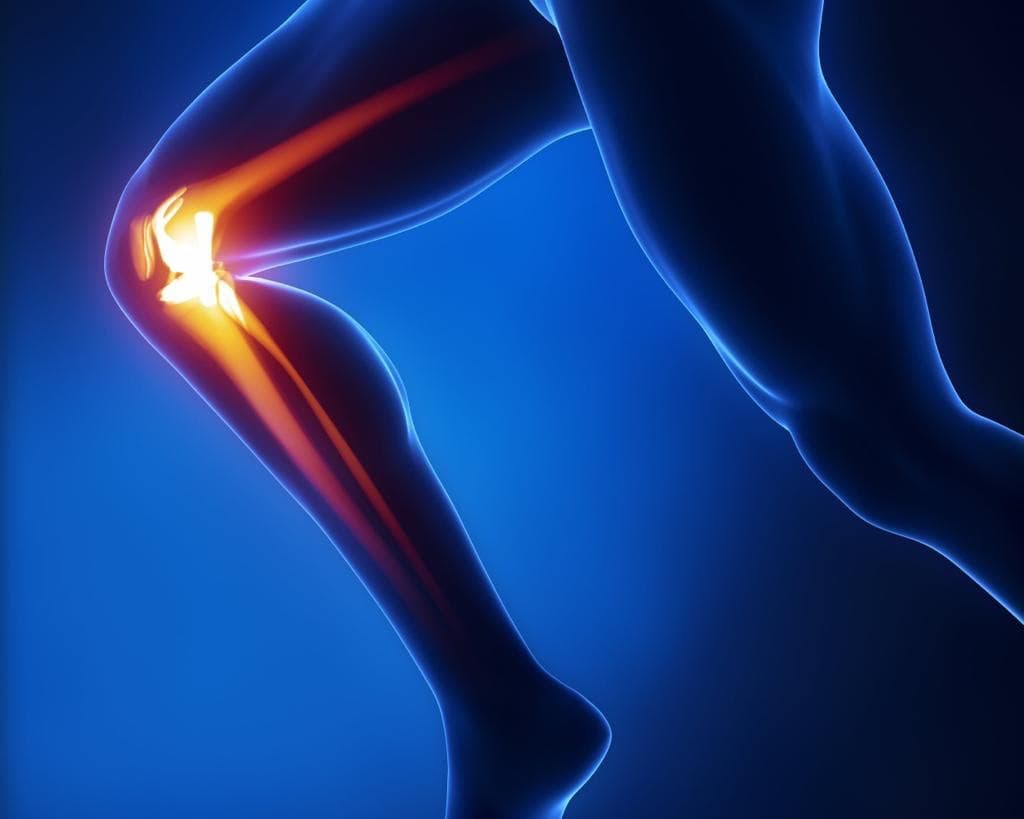
Stages of osteoarthritis :
Advanced odteohealth clinic
Back, neck and knee pain clinic
(photo 18)
- • Stage 0 – Normal
- • Stage 1 – Minor
- • Stage 2 – Mild
- • Stage 3 – Moderate
- • Stage 4 – Severe
When the knee shows no signs of osteoarthritis, it is classified as Stage 0, which is normal knee health, with no known impairment or signs of joint damage.
Stage 1 OA patients will develop very minor wear & tear and bone spur growths at the end of the knee joints. However, at this stage it is unlikely you will feel pain or discomfort.
In Stage 2, diagnostic images or X-rays of knee joints will show more bone spur growth, and though the space between the bones appear normal, people will begin experiencing symptoms of joint pain. Typically, the area around the knee joints will feel stiff and uncomfortable, particularly when sitting for an extended period, after rising in the morning, or after a workout.
Stage 3 is referred to as “moderate”, where there is obvious erosion to the cartilage surface between bones and fibrillation narrows the gap between the bones.
Stage 4 is considered to be severe. In stage 4 the joint space between the bones are considerably reduced, causing the cartilage to wear off, leaving the joint stiff. The breakdown of cartilage leads to a chronic inflammatory response, with decreased synovial fluid that causes friction, greater pain and discomfort when walking or moving the joint.
Jan 2, 2021 What is osteoarthritis ?
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis, affecting millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of your bones wears down over time. Although osteoarthritis can damage any joint, the disorder most commonly affects joints in your hands, knees, hips and spine.
The most common symptoms are joint pain and stiffness. Usually the symptoms progress slowly over years.Initially they may occur only after exercise but can become constant over time.
Knee arthritis is known to affect joint functionality causing knee pain and even leading to disability as it progresses. There are different stages of knee osteoarthritis (OA), with 0 assigned to a normal, healthy knee right up to the advanced stage 4, that is severe OA.
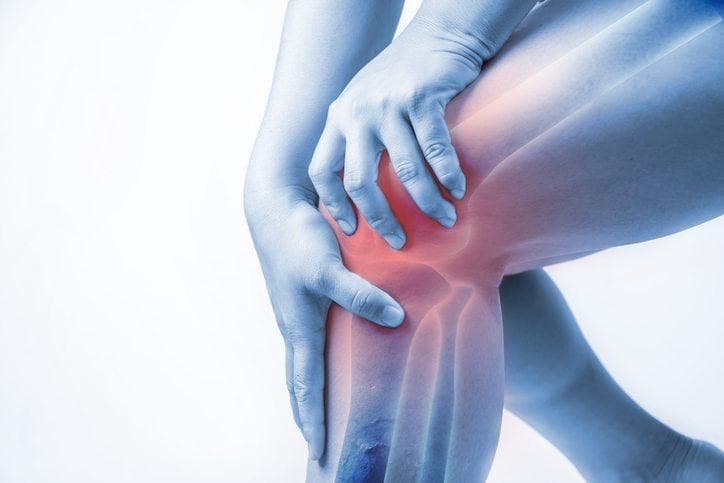
Dec 17, 2020 What is Arthritis ?
Advanced odteohealth clinic
Back, neck and knee pain clinic
(photo 17)
Arthritis is the swelling and tenderness of one or more of your joints. The main symptoms of arthritis are joint pain and stiffness, which typically worsen with age. The most common types of arthritis are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
A reduction in the normal amount of this cartilage tissue cause some forms of arthritis. Normal wear and tear causes OA, one of the most common forms of arthritis. An infection or injury to the joints can exacerbate this natural breakdown of cartilage tissue.
There's no final cure for arthritis, but there are many treatments that can help slow it down. Osteoarthritis treatments include lifestyle changes and medicines and surgery. However in our clinic we aim to treat arthritis naturally and holistically with the use of manual therapy and physical modalities , leaving you feeling Yonge, and pleased.
Nov 30, 2020
